Velocity-based storage and stowage decisions in a semi-automated fulfillment system
本文最后更新于:2022年4月24日 下午
Chapter2 Velocity-based storage decisions
we consider three types of storage policies in this paper:
- random storage policy:随机存储策略
- full-velocity storage policy:基于周转率的存储策略,货架的周转率等于其上物品的需求率之和
- class-based storage policy:分级存储,将存储区域分区,将物品分级,对应存放
2.1 literature Review
疑问:
they set expected duration of stay of the $i^{th}$ storage unit of an item to be i/V for i = 1,2,. . . ,Q, where V is the demand rate of the item and Q is the number of storage units of the item in the system. With the duration of stay policy, the storage units across all the different items can be ordered according to this measure and then assigned in order to the closest locations. Hence, the storage units of a single item may not be stored together in the warehouse.
2.2 Model Assumptions
We establish a fluid model that evaluates the expected travel distance of the pods for their pick tours.
对于某个可移动货架而言,其预计行驶距离=其存储位置到工作站的距离乘以其周转率
Assumptions
- A1: Fluidity of inventory items
对物品进行连续性处理
fluidity:流动性,流畅we index the items (i.e., the stock keeping units) on the continuum from 0 to 1.We assume that the items are indexed in descending order of demand.
按照物品的需求量对仓库内的物品在0到1内进行降序排列。
(Q:是否是需求量占比?)
- A2: Fluidity of inventory units, exponential demand for each item
假设物品的需求量符合指数分布We model the demand of each item as being the number of units required for picking in a specified period of time,e.g.,the next twelve hours.For each item we model the demand as a continuous random variable with an exponential distribution.
定义每个物品的需求量为未来一段时间内该物品的单位拣选量。假设每个物品的需求是服从指数分布的连续型随机变量。指数分布能够反映需求的长尾效应和需求的多变性。
we model the inventory as being continuous, as like a fluid.
- A3: Ranked inventory
对每个物品库存数量进行排序
Thus, if the demand for item i equals x units, then the x -highest ranked units of inventory will be picked to meet the demand.
由于物品分散存储,不同的储位存放的数量可能不一样,对同一商品的不同货位进行排序,当订单到达时,选取库存数量最多的储位满足订单。
A4: Universal stock out rate for all items
所有物品在下一段时间的缺货率相等均为$\alpha$A5: Same unit size for all items, fixed pod size
假设每个货架的储位数量相等,每个物品大小尺寸相等A6: Number of picks independent of the pod’s velocity measure
货架在工作站拣选的物品数量不依赖其周转率,主要关注货架到达工作站的频次A7: Linear travel distance
货架移动距离随着仓库存储空间增多呈线性增长- A8: High space utilization
假设货架数量与仓库存储位置数量相等 - A9: Ignore stow operations
忽略上货操作 A10: Ignore pick-up trip of the robotic drives
忽略AGV取货架的路程2.3 Model Preliminaries
$v_i(x)$表示物品$i$的需求超过$x$的概率(1减去需求指数分布的分布函数CDF),$V_i$表示物品$i$在一段时间内的需求率,不失一般性,令:
f(x)=
\begin{align}
& \lambda e^{-\lambda x}, x\geq 0 \\
& 0, x\lt 0 \\
\end{align}
$$
在这里$\lambda=\frac{1}{V_i}$
指数分布分布函数:$P(X\leq x)=F(x)=1-e^{-\lambda x}$- 定义物品$i$的库存数量为$Q_i$
所有物品在下一时间段的缺货概率为$\alpha$,因此整个仓库的库存数量为:
这里发现假设所有物品有同样的缺货率等同于假设所有物品的库存数量相同。
Hence we can express the days of cover as:
For instance, if the stockout probability were 0.05, then we hold inventory to cover 3.0($\approx\ln0.05$) periods of demand.
- $C$表示货架的货位数,$J$表示货架的数量
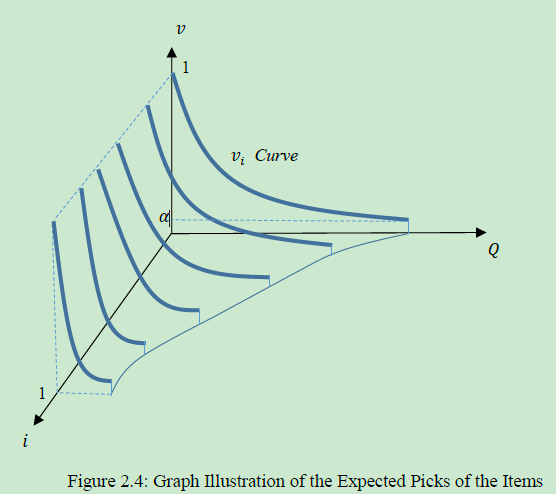
[i轴表示物品,v轴表示物品被订购的可能性,Q轴表示物品的库存数量]2.4Evaluation of Storage Policies under Random Stowage
随机存储策略下的货架布局策略评估Our objective is to evaluate the expected total travel distance under the different storage policies
设定目标函数为预计的总移动距离
根据A3的假设,设$D_i$为下一段时间物品$i$的需求量(被拣选的数量),则:
则其期望与方差$E[D_i],Var(D_i)$:
$U_j^R$表示货架$j$ 的周转率,因为本节讨论的为随机存储策略,所以假设该随机变量对于所有货架($j=1,2,\cdots,J$)是独立同分布的。所以$U_j^R$的期望,对每个货架而言都是$\frac{1}{J}$,因此:
$define:\quad v=\int_0^1V_i^2di$
根据假设A6,我们认为货架去工作站的次数与其周转率$U_j^R$成比例
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!